An E2B USB drive contains an MBR partition on the first sector of the USB drive.
The MBR (Master Boot Record) contains a partition table consisting of four 16-byte entries.
For UEFI-booting, a FAT partition is required, so one of the partitions should be FAT (FAT12/FAT16/FAT32).
The second partition on a typical E2B USB drive will contain a FAT32 partition with the UEFI boot files on it.
The boot file \EFI\BOOT\BOOTX64.EFI is required for UEFI64 booting (or BOOTIA32.EFI for UEFI32 systems).
The UEFI BIOS is more fussy than the old Legacy BIOS about the MBR partition table.
If one or more of the four entries in the partition table is not in ascending order or overlaps another partition entry then the UEFI BIOS will refuse to access the drive and the UEFI shell may ignore one or more of the partition on that drive.
To check the partitions:
- Legacy\MBR boot to the E2B USB drive (tip: you can use QEMU_MENU_TEST (run as admin).cmd under Windows if you don’t have a BIOS system).
- Go to the grub4dos command line (e.g. SHIFT+P – enter password – SHIFT+C)
- On the grub4dos command line type checkptns (hd0) (default is hd0)

Also, on the grub4dos command line type graphicsmode 3 and press ENTER then type display_ptns (hd0) to view the table
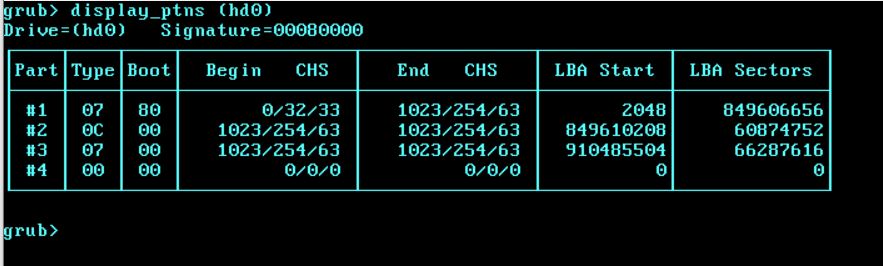

Partitions of Type 0 are ignored by UEFI and Windows.
Note: A typical issue is that you have previously selected a .imgPTN file and it has added/replaced a new partition which is only suitable for Legacy\MBR booting.
In this case, Legacy/MBR boot to the E2B CSM menu and choose the Restore E2B menu option.
Alternatively, type RestoreMBR if you cannot restore the original E2B partitions after using a .imgPTN file.


If all else fails, you can use a disk editor to remove partitions (or use RMPrepUSB to view and edit the MBR).